What are Fricatives?
A fricative is a consonant sound that is created by constricting the vocal tract, causing friction as the air passes through it. The nine English fricative sounds:
often do not correlate exactly with any particular sound in an English as a Second Language/English as a Foreign Language student's native language. This causes substitutions to occur, and those substitutions often have significant differences from the intended English sound.
There are three major points that beginner ESL/ELL students should understand about fricative sounds:
To produce fricatives, air travels smoothly through a small, constricted opening in the vocal tract. The friction of the air causes the sound.
Fricatives are capable of being formed continuously, with no complete blockage of the vocal tract (unlike stops and affricates).
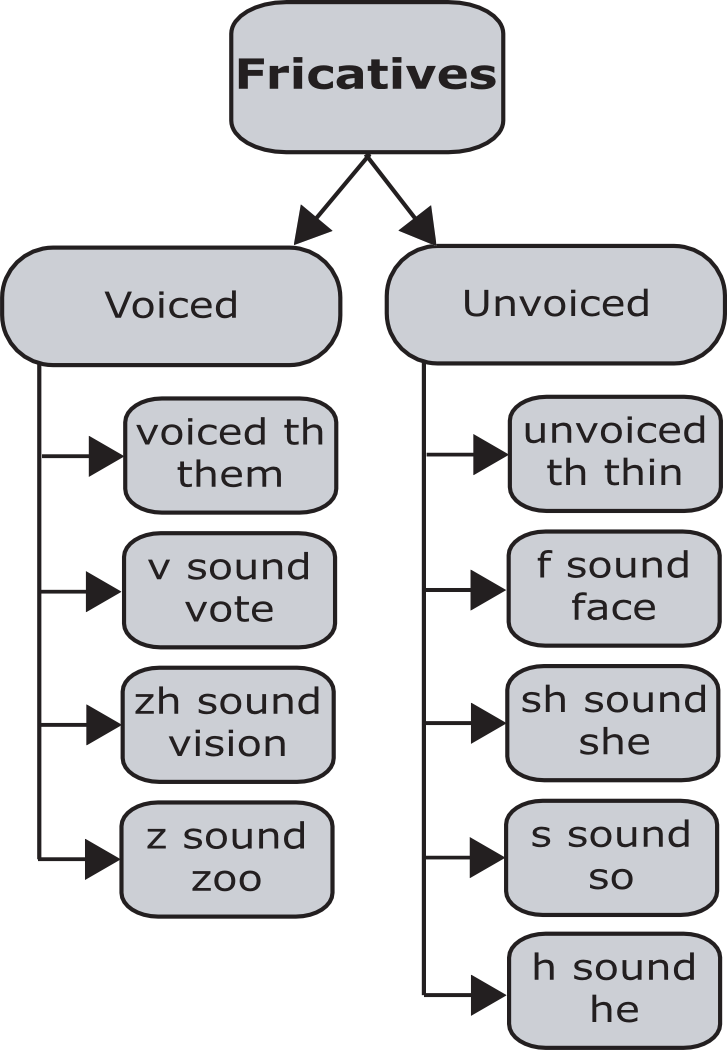
Except for /h/, fricatives occur in voiced/unvoiced pairs.
There is one subtle, additional aspect of fricative sounds:
The duration of a vowel sound before a voiced fricative is greater than the duration of a vowel sound before an unvoiced fricative.
Voiced and unvoiced sounds
Of the nine fricative sounds in English, four are voiced (meaning that the vocal cords vibrate while producing the sound) and five are unvoiced (meaning that the vocal cords do not vibrate while producing the sound). Voiced and unvoiced sounds usually occur in pairs, with the major difference between the sounds in the pair being the use of the vocal cords or not.
Vowel lengthening
The vowel sound before voiced consonant sounds has a longer duration than the vowel sound before its unvoiced counterpart. This change in vowel duration subtly helps listeners of English to determine which fricative sound was spoken. Some dictionaries will use a colon-like symbol of stacked triangles (ː) to note a vowel with increased duration.
Notice the difference in vowel duration in the following minimal pairs.
face /feɪs/ — phase /feɪːz/
bus /bʌs/ — buzz /bʌːz/
safe /seɪf/ — save /seɪːv/
leaf /lif/ — /liːv/
NOTE: Since vowel duration is also influenced by word stress within a sentence, vowel duration due to voicing/unvoicing can be difficult to notice during a conversation.