-ate Suffix Syllable Stress Pattern
The complex and versatile -ate suffix is used to create nouns, adjectives, and verbs. While the primary stress of most words containing the -ate falls on the third-from-last syllable, the suffix itself is pronounced differently depending on the part of speech the word is used in.
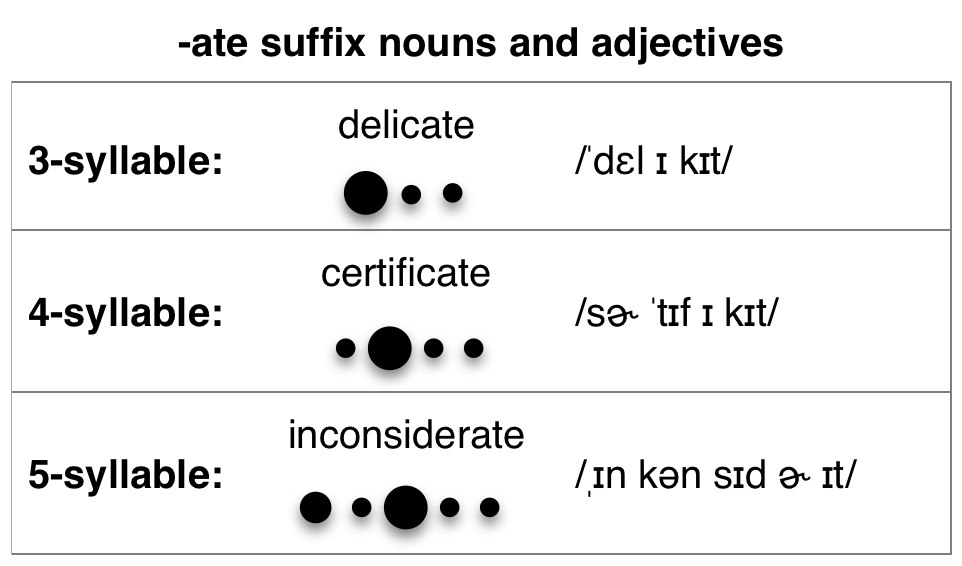
-ate suffix: nouns and adjectives
When a word containing an -ate suffix is a noun or an adjective, the vowel sound of the suffix is unstressed and is pronounced with a short i /ɪ/.
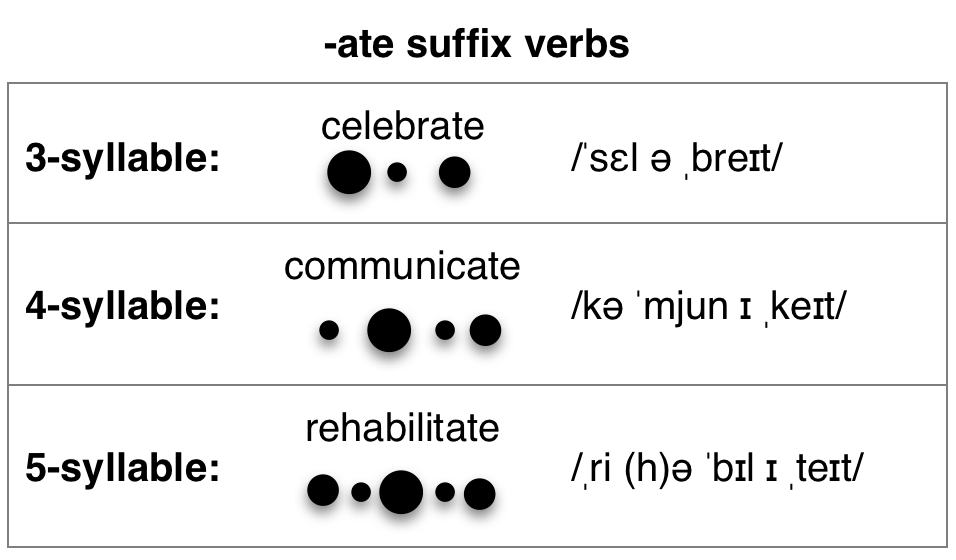
-ate suffix: verbs
When a word containing an -ate suffix is a verb, the vowel sound of the suffix is given a secondary stress and is pronounced with a long a /eɪ/.
Example -ate suffix sentence
The following sentence demonstrates the difference in pronunciation between -ate suffix nouns, adjective, and verbs.
They had to evaluate (verb) the certificate (noun) to be certain that it was accurate (adjective).
-ate + -ly suffix adverbs
Adjectives ending in -ate can have an additional -ly added to them, creating an adverb. The primary stress of the word remains two syllables before the -ate suffix. However, the /t/ of the -ately suffix is usually pronounced as the glottal stop /ʔ/, a /t/ allophone.
-ate suffix Heteronyms
Some words containing the -ate suffix are heteronyms, meaning that a single spelling can have more than one pronunciation. When this occurs in words containing the -ate suffix, the suffix retains the pattern of nouns and adjectives being pronounced as /ɪ/ and verbs being pronounced as /eɪ/.
I'd like to elaborate (verb) on my proposal.
The elaborate (adjective) house had twelve bedrooms and sixteen fireplaces.
-ate suffix heteronym examples
1) advocate:
(n) /ˈæd və kɪt/,
(v) /ˈæd və ˌkeɪt/
2) alternate:
(n/adj) /ˈɔl tɚ nɪt/,
(v) /ˈɔl tɚ ˌneɪt/
3) elaborate:
(adj) /ɪ ˈlæb (ə) rɪt/,
(v) /ɪ ˈlæb ə ˌreɪt/
4) initiate:
(n) /ɪ ˈnɪʃ i ɪt/,
(v) /ɪ ˈnɪʃ i ˌeɪt/
5) graduate:
(n) /ˈgræʤ u ɪt/,
(v) /ˈgræʤ u ˌeɪt/
6) separate:
(adj) /ˈsɛp (ə) rɪt/,
(v) /ˈsɛp ə ˌreɪt/